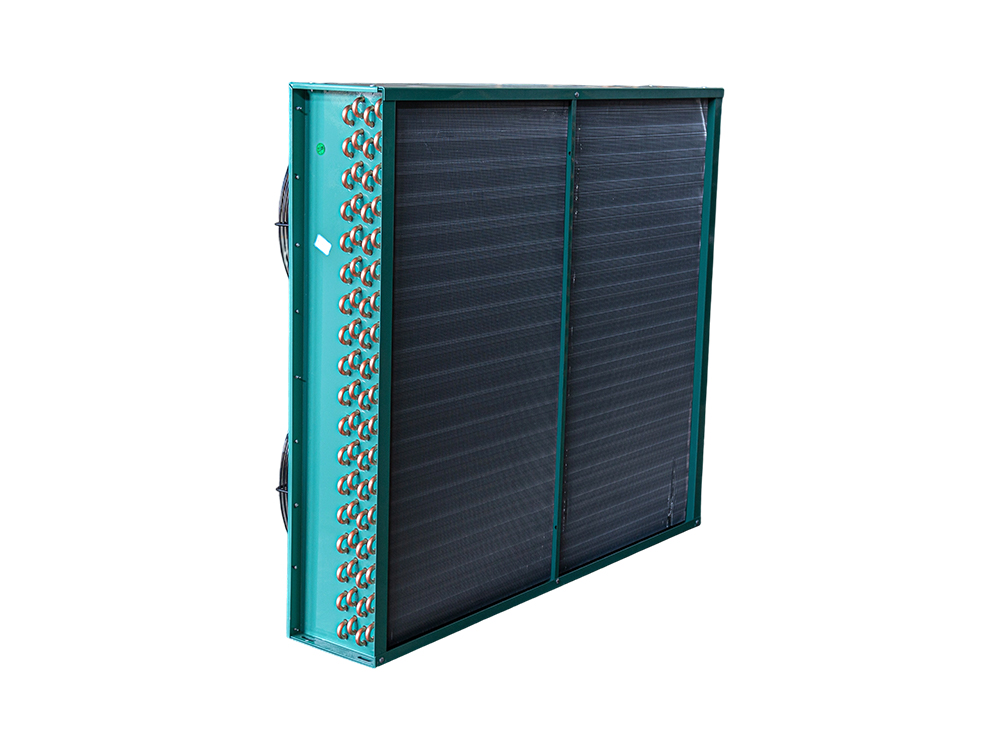
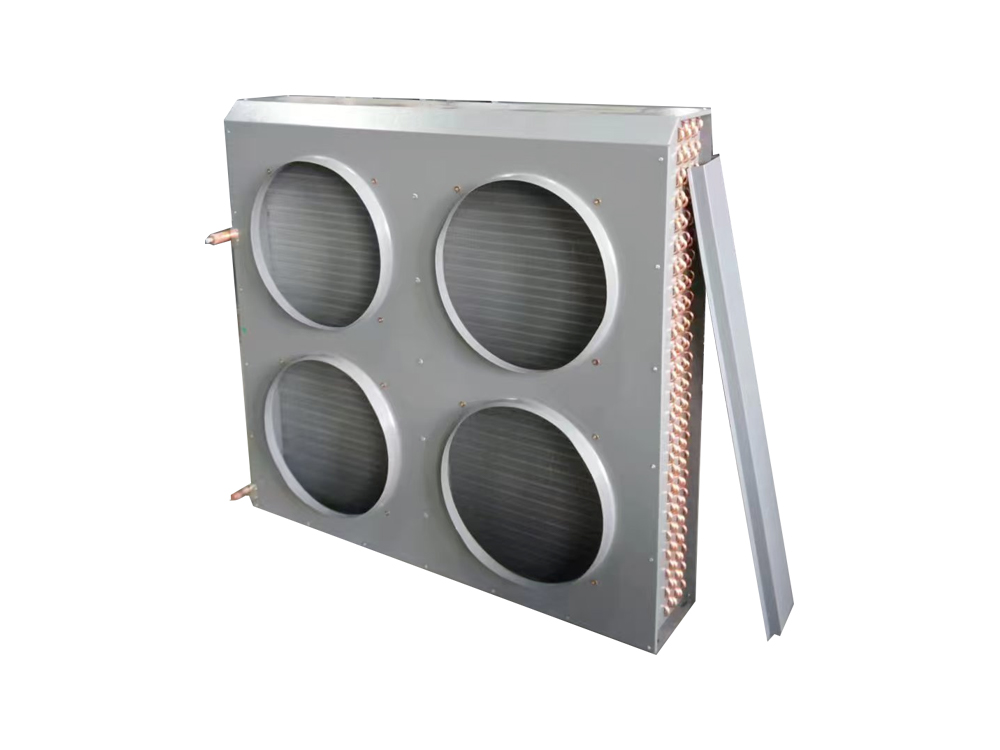
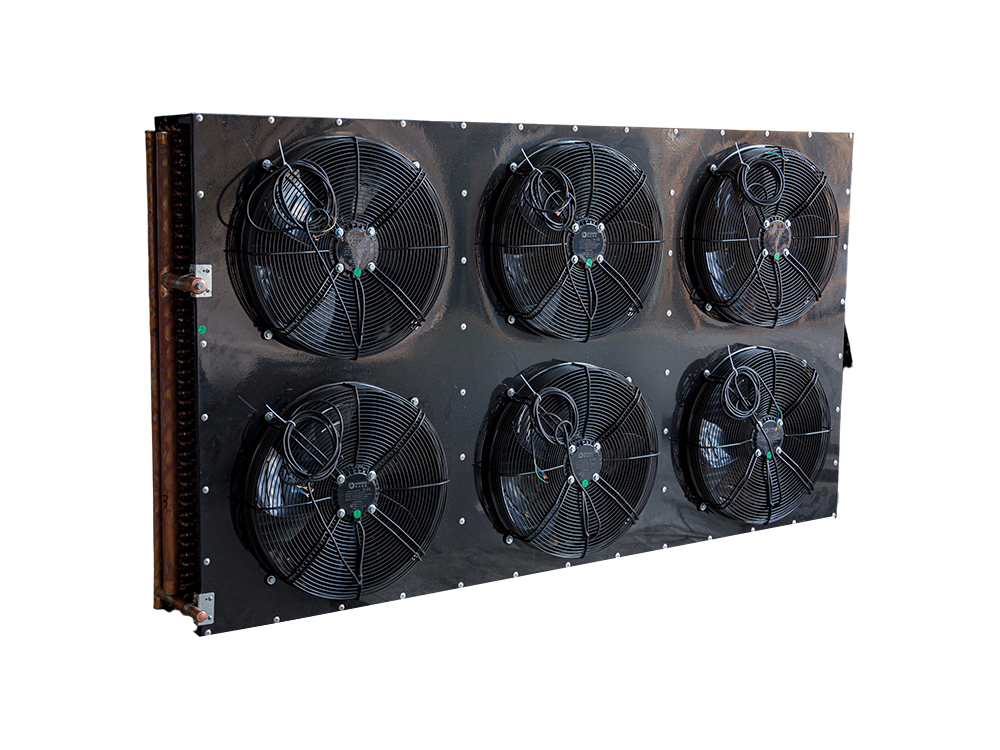
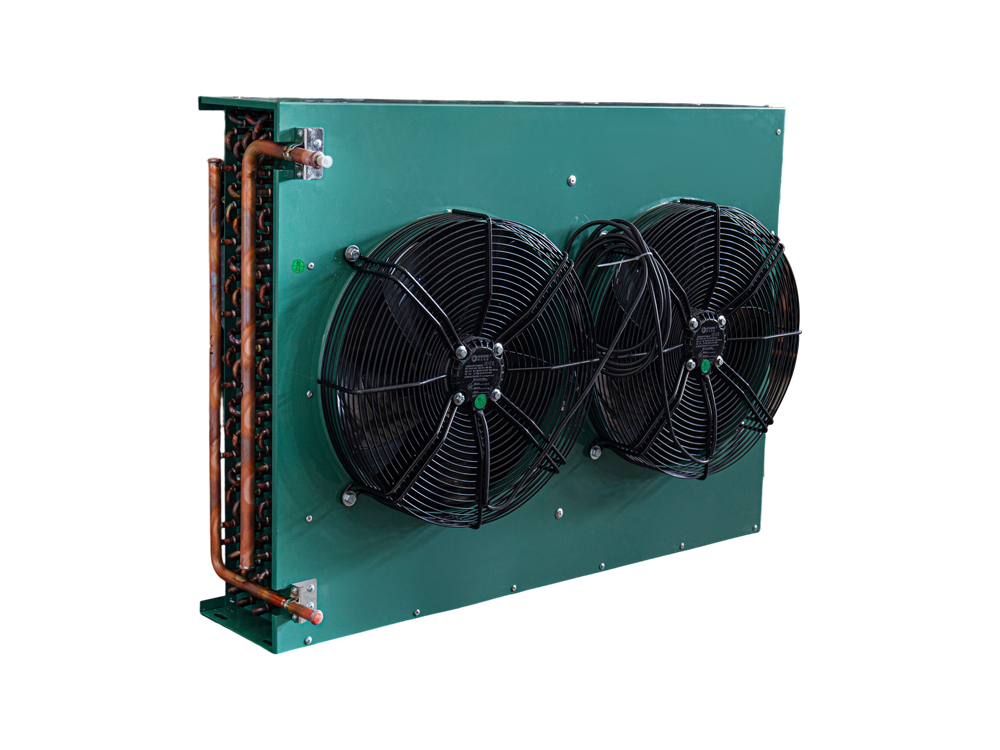
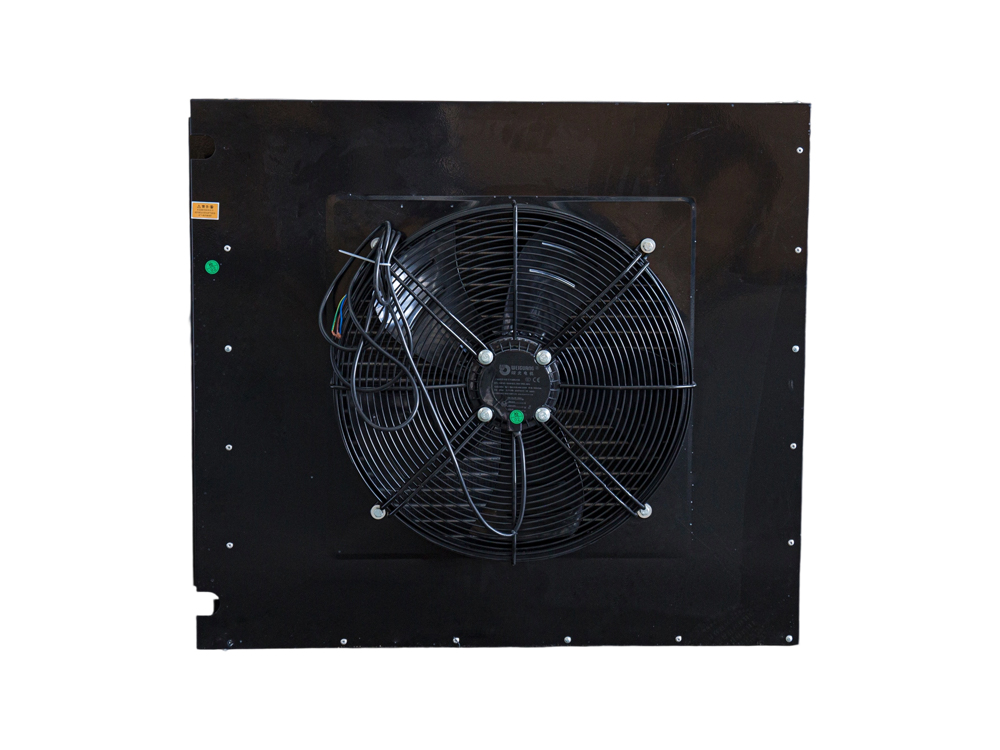
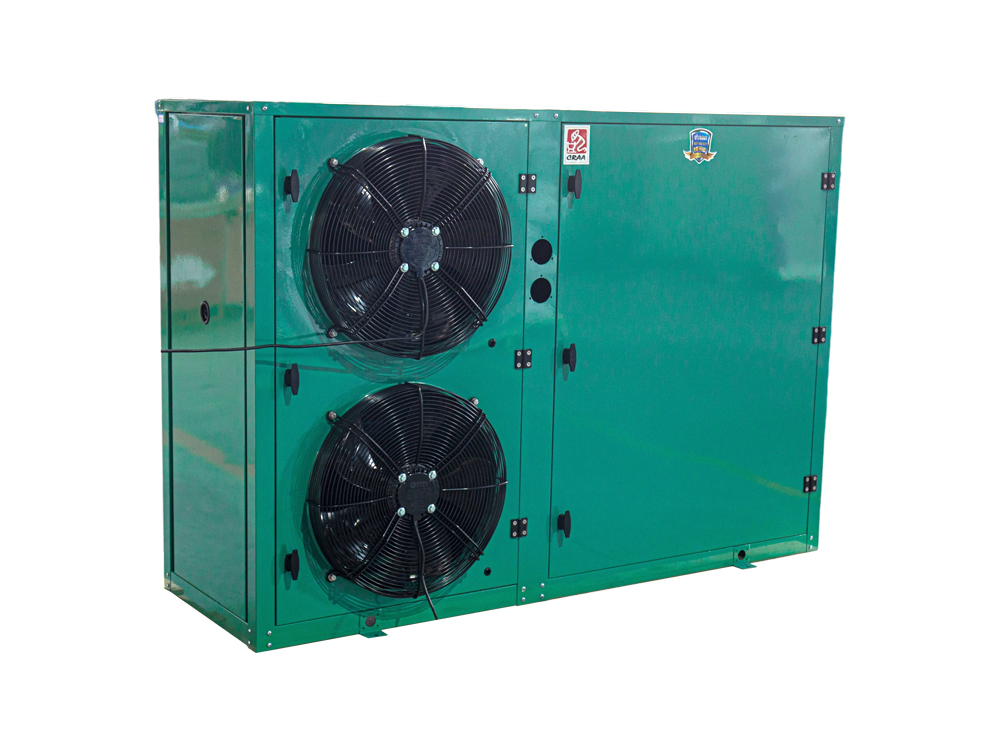
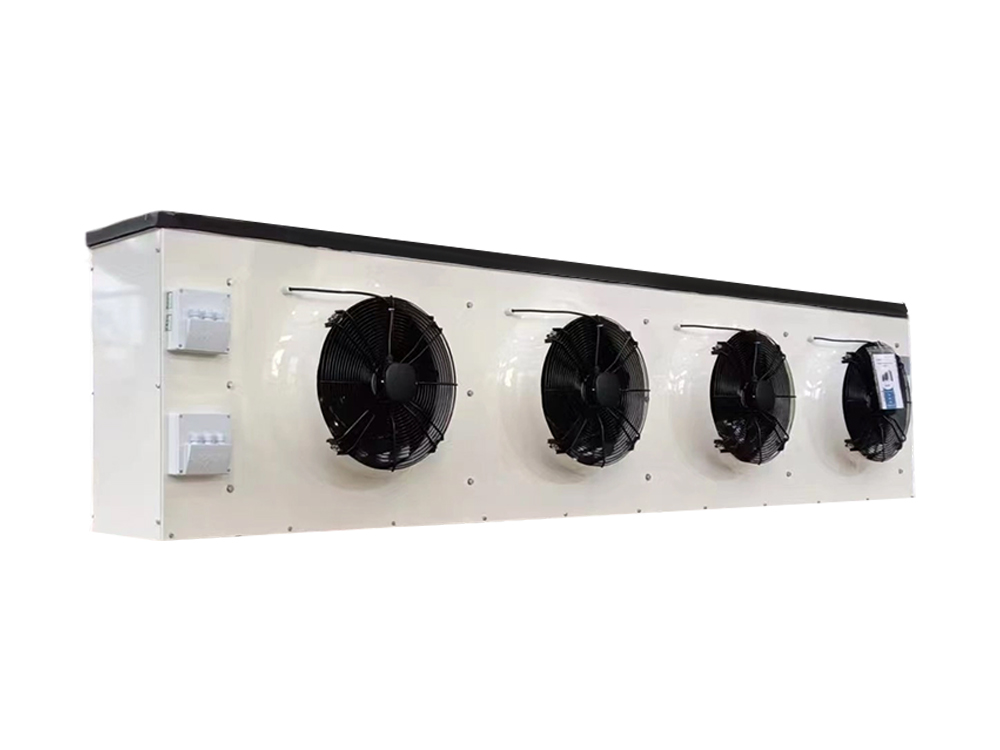
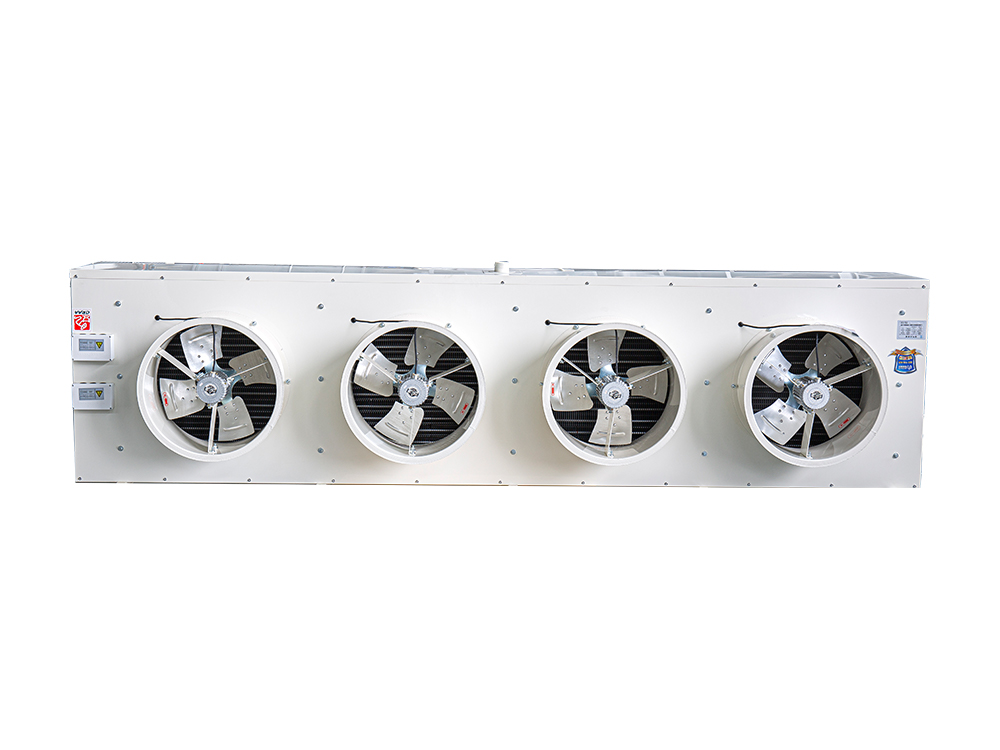
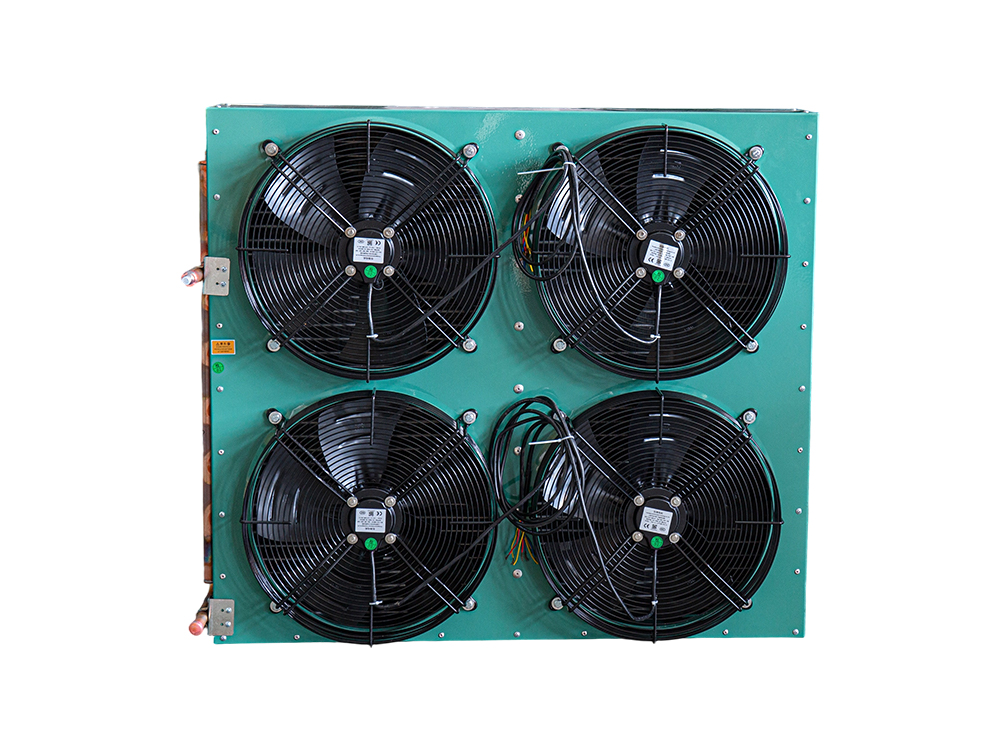
The four-air plate H-type condenser is a heat exchange device that utilizes a multi-channel plate structure. Its core consists of a series of parallel corrugated plates, forming efficient refrigerant condensation channels. This structure increases heat transfer efficiency by increasing the heat exchange area and enhancing fluid turbulence. The outer shell is typically constructed of corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy or galvanized steel (iron), while the internal plates are mostly galvanized iron, though stainless steel can also be added to meet the corrosion resistance requirements of different operating conditions.
The device features a four-air inlet design, supporting multi-directional air inlet and outlet configurations, adapting to diverse system layout requirements. The fan is typically equipped with an external rotor motor or EC motor with stepless speed regulation, automatically adjusting air volume based on system load. The H-shaped structural frame ensures overall rigidity while facilitating modular expansion and maintenance.
This condenser is suitable for medium-to-large refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pump systems. It operates stably in ambient temperatures ranging from -30°C to 50°C and has a maximum operating pressure of 4.5 MPa (modified to 2.8 MPa). Its design focuses on matching the processes of the compressor and evaporator, and supports a variety of common refrigerants such as R410A, R32, R134a (modified into R22, R404, R507), etc.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español